With the extensive use of routine prenatal ultrasound, many conditions or abnormalities are now being identified before the baby is born. If you had an ultrasound during your pregnancy and were told that your baby had hydronephrosis, this condition will need to be evaluated when your baby is born.
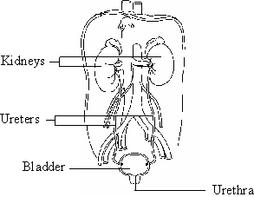
Hydronephrosis refers to a dilatation or an "over-accumulation" of urine in the portion of the kidney, where urine is collected. It may involve one or both kidneys.
Hydronephrosis is the most common abnormality detected on prenatal ultrasound.
What causes hydronephrosis?
There are several possible causes of hydronephrosis. Some of the known causes include:
- An obstruction or blockage where the ureter joins the kidney
- An obstruction where the ureter joins the bladder
- Vesicouretal reflux (the backflow of urine from the bladder to the kidney)
- A ureterocele (an outpouching of the ureter in the bladder)
- Posterior urethral valves (valves in the urethra that can cause blockage with urine backing up all the way to the kidneys)
- Having two ureters drain the kidney, with a blockage or reflux affecting one of them
- A variation of normal anatomy
In most cases, the cause may not be determined before the birth of the baby.
How is hydronephrosis taken care of during pregnancy?
Most cases of hydronephrosis remain stable throughout pregnancy. Some cases may correct themselves and some may worsen. As long as the hydronephrosis does not worsen significantly and the amount of amnionic fluid is adequate, the pregnancy will be monitored with ultrasounds at frequent intervals and no special treatment is necessary before the baby is delivered.
What happens after the baby is born?
Often babies with hydronephrosis detected on prenatal ultrasound will be started on a preventative antibiotic until the postnatal evaluation is completed. Depending on the degree of hydronephrosis, further evaluation of the baby may be necessary. This may include:
- An ultrasound of the baby's bladder and kidneys
- A voiding cystourethrogram (VCUG): A study to evaluate the bladder for reflux and to evaluate the urethra
- A renal scan to determine if there is a blockage or an obstruction
Page reviewed on: Apr 29, 2009
Page reviewed by: Leslie T. McQuiston, MD